
本文根据savemyexams, 课上的笔记和网络上的信息整理而来
虽说我尽量把我所学的所有IG化学知识都记录在此。但难免有疏漏,最好考前看一眼syllabus: here
标注为(!)的部分代表此部分笔记为课堂笔记整理而来,并没有对照savemyexams或者syllabus检查过全面性
(差异有点大就以老师的为准了(逃)),需要读者自行验证本文原先使用Typora撰写,其中有些拓展语法(如高亮==, 上标^, 下标~) fuwari并不支持
(而我也懒得改成LaTeX了),请见谅QAQ所以如果有任何错误/补充欢迎评论指正
Table of Content:
- 1. States of Matter
- 2. Atoms, Elements & Compounds
- 3. Stoichiometry
- 4. Electrochemistry
- 5. Chemical Energetics
- 6. Chemical Reactions(!)
- 7. Acids, Bases & Salts
- 8. The Periodic Table
- 9. Metals
- 10. Chemistry of the Environment
- 11. Organic Chemistry
- 12. Experimental Techniques & Chemical Analysis
1. States of Matter
1.1 Solids, Liquids & Gases
1.1.1 Kinetic Theory(..)
| solids | liquids | gases | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Volume | fixed | fixed | not fixed |
| fixed shape | adopt the shape of the container | adopt the shape of the container | |
| high density | middle | low density | |
| regular pattern | randomly arranged | randomly arranged | |
| vibrate around a fixed position | move around each other | move quickly and randomly in all directions | |
| low energy | greater energy | highest energy |
1.1.2 States of Matter
two points: melting point and boiling point

| boiling | evaporating |
|---|---|
| boiling point | a range of temp |
| bubbles below the surface | surface |
range of temp: Condensation, evaporating
sublimation: only a few solids(CO2,I2)
reversible arrow: ⇌
1.1.3 Pressure & Temperature in Gases
Ideal Gas Law:
1.1.4 Diffusion
==Diffusion==: Particles move down the concentration gradient (?)
温度越高,diffusion越快
random motion of particles
high concentration -> low concentration
the concentration is even as they spread out
relative molecular masses
NH3 + HCl -> NH4Cl
HCl > NH3
一些gas的论证:(vaporised 后)move randomly in the container, no forces between gaseous molecules(没有力支撑,液体就有支撑), molecules can move apart(液体就不行)
2. Atoms, Elements & Compounds
| Structure | Bonding | 组成 | Graph(记得label !) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Giant Ionic | Ionic Bond | Metal + Non-metal | [ ]+ [ ]- 或者正负离子交替 |
| Giant Metallic | Metallic Bond | Metal | lattice的cations还有sea of delocalised e- |
| Giant Covalent | Covalent Bond | Diamond, Graphite, SiO2 | 一般不画 |
| Simple Molecular | Covalent + Inter Molecular Forces | Non-metal | 像文氏图,然后画电子(need = share) |
| Structure | Electrical Conductivity | Reason | m.p. / b.p. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Giant Ionic | l / aq (molten / aqueous state) | Mobile Ions | High (Strong ionic bond between oppositely charged ions) |
| Giant Metallic | s / l | Delocalised e- | High (Strong metallic bond between cations & delocalised e-) |
| Giant Covalent | only graphite | Delocalised e- | High (Strong covalent between atoms) |
| Simple Molecular | x | Low (Weak IMF between molecules) |
2.1 Atomic Structure & the Periodic Table
2.1.1 Elements, Compounds & Mixtures
Element: 元素
Compound: 化合物
Mixture: 混合物
可以继续分为homogeneous mixture(质地统一) / heterogeneous mixture(不统一)
2.1.2 Atomic Structure
Subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, electrons
nucleus: 原子核
relative atomic mass: 相对原子质量
Atomic number(Z): protons
Nucleon Number / mass number (A): protons + neutrons
Atomic notation: A上Z下
2.1.3 Electronic Configuration
表示原子结构两种方式:electron shell diagrams, electronic configuration (electronic structure)
离原子核越远,电子层能量越高
the outermost shell = the valence shell最外层
period: number of notations
group: last notation
最外层电子:valency electrons
2.1.4 Isotopes
Isotopes: different atoms of the same element (that contain the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons)
表示法:C-14(mass number)
化学性质相似:相同的最外层电子
物理性质差异:不同的原子质量
2.2 Ions & Ionic Bonds
2.2.1 Ions & Ionic Bonds
Ion: An electrically charged atom or group of atoms formed by the loss or gain of electrons
负离子:anion
正离子:cation
ionic bond: strong electrostatic forces of attraction between opposite charges
dot-and-cross diagram: 元素外打括号,右上角写电荷。(只用画最外层电子)记得配平(前面写系数)
2.2.2 Ionic Bonds & Lattice Structure
lattice structure: ordered, repeating, regular arrangement of alternating anions and cations.
2.2.3 Properties of Ionic Compounds
solid at r.t.
high m.p. and b.p. (strong electrostatic forces)
good conductors of electricity in the molten state or in solution
poor conductors in the solid state
2.3 Simple Molecules & Covalent Bonds
2.3.1 Covalent Bonds
Covalent bond: pairs of electrons are shared between atoms(只有non-metal elements)
Molecules: two or more atoms are covalently bonded together
画dot-and-cross diagram: 两个圆相交部分画电子
single covalent bond(single bond)只share一对电子
2.3.2 Molecules & Compounds
double bond / triple bound
2.3.3 Properties of Simple Molecular Compounds
Simple molecular compound: just a few atoms covalently bonded together
low m.p. and b.p. (如果分子更大m.p.和b.p.也更大) (因为week intermolecular forces弱分子间作用力)
poor electrical conductivity(no free ions or electrons)(可作为insulator)
2.4 Giant Structures
Diamond & Graphite(石墨)
Allotropes(同素异形体): Different atomic or molecular arrangements of the same element in the same physical state
Diamond: 接四个 form a tetrahedron(四面体)
no intermolecular forces
Graphite: 接三个 form layers of hexagons
layer之间:weak intermolecular forces
unpaired electron becomes delocalised
Properties & Uses
Diamond:
don’t conduct electricity
high m.p.
extremely hard and dense
uses: jewellery, cutting tools
Graphite: can conduct electricity, slippery and smooth, high m.p.
pencil
industrial lubricant(润滑剂)
non-reactive electrods for electrolysis(conduct electricity, high m.p., inert(stable), cheap)
2.4.2 Silicon(IV) Oxide
Quartz: 石英
结构:钻石的结构。碳变为硅,键上面放一个氧
性质:类似于钻石,更便宜
用途:sandpaper,
2.4.3 Metallic Bonding
metallic lattice
electrons delocalised
sea of electrons
Properties:
high m.p. and b.p.
conduct electricity
malleable(可塑性)
Ductile(可延展性)
(layers of positive ions can slide over one another and take up different positions)
wire
3. Stoichiometry
(化学计量法)
Solid: (m单位g , Mr单位g mol-1)
Liquid: (c单位mol dm-3 , V单位dm3)
Gas: (V单位dm3, 24单位dm3 mol-1)
3.1 Formulae & Relative Masses
3.1.1 Formulae
diatomic molecules: 双原子分子
3.1.2 Empirical Formulae & Formulae of Ionic Compounds
Empirical formula: 实验式
polyatomic: 多原子的
3.1.3 Writing Equations
reactants: 反应物
products: 生成物
- Solid = (s)
- Liquid = (l)
- Gas = (g)
- Aqueous = (aq)
Precipitates: 沉淀
3.1.4 Ar & Mr
Ar: relative atomic mass
Mr: relative molecular mass
(对于ionic compound是relative formula mass)
3.2 The Mole & the Avogadro Constant
3.2.1 The Mole
The mole: the SI unit of amount of substance
Avogadro Constant: 6.02e23
molar mass: 一摩尔的物质的质量(gram)在数值上等于相对质量
Avogadro’s Law: same temperature and pressure, 相同数量气体占的空气相等
常温常压1mol气体占24dm3 / 24000cm3空间(molar gas volume at RTP)
3.2.2 Linking Moles, Mass & Mr
n = m / Mr
3.2.3 Reacting Masses
limiting reactant: the reactant that is used up first
excess reactant: the one that is remaining
3.2.4 Calculating Concentration
Solute(溶质): a solid substance that dissolves into a liquid
Solvent(溶剂): the liquid that a solute dissolves in
concentration: the amount of solute there is in a specific volume of the solvent(g/dm3 & mol/dm3)
3.2.5 Titration Calculations
3.2.6 Empirical & Molecular Formula
Hydrated salt: a crystallised salt that contains water molecules as part of its structure
3.2.7 Percentage Yield & Purity
Yield: the term used to describe the amount of product you get from a reaction
percentage yield = actual yield / theoretical yield
percentage composition:
Percentage purity
4. Electrochemistry
4.1 Electrolysis
==Electrolysis==: Break down ionic compounds in molten / aqueous state by electricity
4.1.1 Electrolysis Principles
molten / aqueous
ionic compounds
electrode: a rod of metal(platinum) or graphite through which an electric current flows into or out of an electrolyte (conductor, inert)
electrolyte: the ionic compound in a molten or dissolved solution that conducts the electricity
-> Molten Salt
-> Conc / dilute solution
-> Copper electrodes
anode: the positive electrode of an electrolysis cell
anion: negatively charged ion
cathode: the negative electrode of an electrolysis cell
cation: positively charged ion
anode: non-metals (在没有conc的情況oh先氧化,否则halogen先)
cathode: hydrogen / metal
PANIC(Positive is Anode Negative Is Cathode)
AN OX / RED CAT (Anode Oxidation / Reduction Cathode)
Shiny: Nickel, chromium
4.1.2 Electrolysis of Molten Compounds
binary ionic compound: consisting of just two elements joined together by ionic bonding
4.1.3 Electrolysis of Aqueous Sodium Chloride & Dilute Sulfuric Acid
brine: concentrated solution of aqueous sodium chloride
gas test for chlorine: if damp litmus paper is dipped into a sample of the gas, it will turn red and then bleach to a white colour
4.1.4 Electrolysis of Aqueous Solutions
ammeter: 电流表
两个电极都是铜,液体是硫酸铜:硫酸铜浓度不变,电极质量变化
4.1.5 Ionic Half Equations
Oxidation: loss of electrons
Reduction: gain of electrons
4OH- -> O2 + 2H2O + 4e-
OIL RIG(Oxidation Is Loss, Reduction Is Gain)
RED CAT(Reduction at the Cathode)
AN OX(Anode for Oxidation)
4.2 Applications of Electrolysis
4.2.1 Electroplating
Electroplating: the surface of one metal is coated with a layer of a different metal
cathode: object to be electroplated
anode: made from the pure metal that will be plated onto the object
Reason: make metals more resistant to corrosion or damage
4.2.2 Hydrogen Fuel Cells
fuel: a substance which releases energy when burned
Advantages:
Renewable, no pollution, release more energy per kg, no power is lost in transmission, quieter
Disadvantages:
expensive, hydrogen is more difficult and expensive to store compared to petrol(flammable and easily explodes when under pressure), affected by low temp
5. Chemical Energetics
5.1 Exothermic & Endothermic Reactions
5.1.1 Endothermic & Exothermic Reactions
system: the reacting chemicals
surroundings: anything other than the reacting chemicals
和acid反应,carbonate可以是exo或者endo,metal只能exo
Exothermic Reaction: 放热
==Definition==: An exothermic reaction transfers thermal energy to the surroundings leading to an increase in the temperature of the surroundings.
e.g.: Neutralization, oxidation, combustion(燃烧反应), dissolving anhydrous salts, reaction between acids and metal carbonates, dissolving crystalline salts(?)
application: hand warmers, self-heating cans
\Delta H < 0
Endothermic Reaction: 吸热
==Definition==: An endothermic reaction takes in thermal energy from the surroundings leading to a decrease in the temperature of the surroundings.
e.g.: Atomization(变成原子?), Electrolysis, thermal decomposition, the first stage of photosynthesis(光合作用),
Application: cold packs
\Delta H > 0
Reaction pathway diagram(reaction profiles)
peak: transition state / activated complex

5.1.2 Enthalpy Change & Activation Energy
原子或分子想要反应要撞在一起。影响因素有能量,方向,频率…
Definitions
Enthalpy(H)(kJ/mol): an indication of the total energy of a substance and it cannot be measured directly.
==Enthalpy change== of a reaction(): The transfer of thermal energy during a reaction.
is negative for exothermic reactions and positive for endothermic reactions.
*Energetic stability of a system
Exothermic reactions are more energetically favorable(likely to happen) than endothermic ones because a system with lower energy content is more stable.
Lower energy state -> more stable
Standard enthalpy changes
Standard enthalpy changes:
Standard condition(°-结合在一起): To make comparison of enthalpy changes a fair comparison, same conditions must be used.
Pressure: 101kPa
Temperature: 298K
Concentration of solutions: 1.0 mol / dm3
Normal physical state
Allotropes: 选更energetically stable的 (选石墨不选钻石)
Activation Energy
==Definition==: The minimum energy that colliding particles must have to react
EA(forward):从reactants到顶峰的能量
EA(reverse):从products到顶峰的能量
5.1.3 Bond Breaking & Bond Forming
Bond Energy(Bond enthalpy): Energy required to break a mole of (covalent) bonds in the gaseous state. (always positive())
有些bond energy是确定的有些取平均(被其他原子的存在所一项
breaking bonds: needs energy (endothermic)
forming bonds: releases energy (exothermic)
Bond breaking:
the energy needed to break bonds
Energy change = Energy required to break bonds - Energy given out when bonds are made(左边减去右边)
6. Chemical Reactions(!)
6.1 Chemical Change & Rate of Reaction
6.1.1 Physical & Chemical Changes
Physical changes: Changes in which new chemical substances are not produced
e.g. change in states, separation of mixtures …
Chemical changes: changes in which new chemical substances are produced
e.g. Decomposition, electrolysis, respiration, photosynthesis, polymerisation, combustion, etc.
6.1.2 Rates of Reaction Factors
study of chemical reactions -> reaction kinetics
Rate of reaction
Rate = change in amount of reactants or product / time
Unit: mol dm^-3^ s^-1^ / mol dm^-3^ min^-1^ / mol dm^-3^ h^-1^
change in amount
-> volume of gas
-> concentration of reactants or products
Measuring rate of reaction
Acidity:
Volume:
Mass:
Appearance:
Electrical conductivity:
Calculation of the rate of reaction
gradient / tangent line
rate of reaction = d[reactant或者product] / dt
reactant的话要取负的gradient
6.1.3 Collision Theory
Heterogeneous reactions: 不同phase之间的物质的reaction
Reaction:
-> particles must collide
-> in the correct orientation and with sufficient energy
Activation Energy: The minimum energy required for a reaction to occur (EA)
Ineffective Collision: takes place if the colliding particles do not have enough energy to react (low K.E.)
Effective(successful) Collision: takes place if the colliding particles do have enough energy to react (high K.E.)
sme上的定义(?): A successful collision is where the particles in the reactant(s) are rearranged to form the products
Speeding up a reaction -> increase rate -> increase effective collision -> (breakpoint) increase collision frequency -> Concentration / Pressure / Surface Area / Temperature
(breakpoint) increase # of particles with E > EA -> Temperature / Catalyst
Energy of molecules -> directly proportional to their absolute temperature
distribution of energies between different molecules: Boltzmann distribution (not all of the particles have the same amount of k.e. )
(一个横轴molecular energy 纵轴number of molecules的图。在竖线EA右边的部分可以参与反应)
-> The distribution always goes through the origin
-> The curve approaches the x-axis but does not touch it
-> The peak represents the most probable energy.
-> The area under the curve represents the total number of particles.
-> The shaded portion represents the number of particles with energy higher than or equal to the activation energy (E>=EA)
The Effect of Concentration and Pressure
frequency of collisions 正相关
不改变Boltzmann distribution of energies
The Effect of Surface Area
和Frequency of Collisions 正相关
不改变Boltzmann Distribution of Energies
The Effect of Temperature
-> 改变Temperature -> 改变particles的K.E. -> 改变速度快慢 -> 改变 Collision Frequency
-> 增加或减少有E大于等于EA的particles
-> 总结:改变frequency of effective collisions
温度增加:most probable energy更高,但更少的粒子达到了这个要求
反之亦然
Rate翻倍只要Temp加十就好了(有点像dB+3
temp可以影响reactants的初始enthalpy(在endo exo那个图里面上移下移)
The Effect of Catalyst
Catalyst: increases(?) the rate of reaction by providing an alternative reaction path way with lower EA
How: more particles have E>=EA, so increase in frequency of effective collisions
催化剂的化学性质反应前后不改变
在Boltzmann图面就是EA往左移,在endo exo的图里就是peak向下移
6.1.4 Explaining Rates Using Collision Theory
6.1.5 Investigating The Rate of a Reaction
6.1.6 Interpreting Data
6.2 Reversible Reactions & Equilibrium
==Equilibrium==: The rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction + the concentrations of reactants and products are no longer changing
reversible reaction: one which can proceed in both directions, as indicated by the “你知道是啥” sign
re-form
equilibrium mixture (in balance)
Dynamic Equilibrium: Rates of forward and reverse reactions are equal in a closed system. (No net change in concentration of reactants and products. (constant concentration))
Equilibrium position: the relative amount of products and reactions present in an equilibrium mixture (mixture of reactants and products)
Le Chatelier’s Principle: If a change is made to a system at dynamic equilibrium, the position of equilibrium moves to minimise this change.
-> 增减一个反应物会反作用(syllabus上说的是改变concentration,也就是说加pure solid和pure liquid也不会改变平衡位置(bestchoice)。存疑)
-> pressure: 会影响气体,看反应物和生成物的摩尔数。会倾向于操作的相反
-> temperature: 看是exo还是endo。倾向于操作的相反
-> catalyst: 不影响equilibrium, 加速到达equilibrium的速度
shift equilibrium to the left / right
Haber process - Ammonia Production: N2(g) + 3H2(g) <-> 2NH3(g); ΔHr = -92 kJmol^-1^
| Factors | Equilibrium Aspects | Industrial Aspects |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Low | 450 C |
| Pressure | High | 200 atm |
| Concentration(NH3) | Removal of NH3 | Liquify NH3 |
| Catalyst | Yes | Iron(Fe) |
N2: Fractional distillation of liquid air
H2: CH4(methane) + H2O(g) -> 3H2 + CO
450: Compensate temperature (太低:increase in yield, low rate of reaction(低KE,低frequency))
200: Compensate Pressure (太高:increase in yield, increase in operating cost / expensive)
Contact process - sulfuric acid production
-> S + O2 -> SO2 (buring sulfur or roasting sulfide ores)
-> 2SO2(g) + O2(g) <-> 2SO3(g) (竟然是reversible的,必须制裁!)
-> SO3 + H2O -> H2SO4 (* SO3 + H2SO4 -> H2S2O7 ; H2S2O7 + H2O -> 2H2SO4)
| Factors | Equilibrium Aspects | Industrial Aspects |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Low | 450 C |
| Pressure | High | 2 atm |
| Concentration | Removal of SO3 | Absorbed by conc. H2SO4 |
| Catalyst | Yes | Vanadium Oxide, V2O5 |
为什么Temperature和Pressure的值都不太低/高呢?和haber process的原因一样。需要compensate
Factors:
->
6.2.1 Reversible Reactions
6.2.2 Equilibrium
6.2.3 The Haber Process
6.2.4 The Contact Process
6.3 Redox(!)
==Disproportionation== : a redox reaction in which both oxidation and reduction occurs on the same atom(it is simultaneously oxidised and reduced)
O不是-2的特例:F2O (+2), H2O2 (-1)
H不是+1的特例:和某个金属结合(metal hydride) NaH
| Formula | Common Name | Name |
|---|---|---|
| NO | Nitrate ion | Nitrate ion |
| NO | Nitrite ion | Nitrate ion |
| NO | Nitrogen dioxide | Nitrogen (IV) |
| SO | Sulfate ion | Sulfate (VI) |
| SO | Sulfite ion | Sulfate (IV) |
| SO | Sulfur dioxide | |
| SO | Sulfur trioxide |
MnO4- : manganate(VII)
6.3.1 Oxidation & Reduction
Roman numeral: 用来indicate the oxidation number of an element in a compound
定义表
Redox reactions: involving simultaneous oxidation and reduction / involving gain and loss of electrons
==Oxidation==: gain of oxygen / loss of electrons / an increase in oxidation number
==Reduction==: loss of oxygen / gain of electrons / a decrease in oxidation number
identify redox reactions by changes in oxidation number …
Oxidation number: a number assigned to an atom or ion in a compound, showing the number of electrons that an atom
6.3.2 Redox & Electron Transfer
==Oxidising agent==: A substance that oxidises another substance and is itself reduced
Very powerful: Acidified Potassium Manganate(VII): KMnO4
MnO4- + 8H+ + 5e- -> Mn2+ + 4H2O
pink -> colourless(?)
==Reducing agent==: A substance that reduces another substance and is itself oxidised
Very powerful: Potassium Iodide:
2I- -> I2 + 2e-
colourless -> brown(?)
加starch变深蓝
7. Acids, Bases & Salts
ethanoic acid: 乙酸
ethanoate: 乙酸根(比如Magnesium Ethanoate)
7.1 The Characteristic Properties of Acids & Bases
base是碱,alkali是可溶解于水的碱
7.1.1 Properties of Acids & Bases
Acids
pH<7
sour taste
corrosive
Reactivity series: K,Na,Ca,Mg,Al,(C),Zn,Fe,Sn(Tin),Pb,(H),Cu,Ag,Au,Pt
Acid + Metal -> Salt + Hydrogen(置换)
acid + base -> salt + H2O(neutralisation)
acid + metal carbonate -> salt + CO2 + H2O
indicators(酸碱指示剂)
| Indicator | Colour in acid | Colour in alkali |
|---|---|---|
| Litmus(石蕊) | red | blue |
| Thymolphthalein | colourless | blue |
| Methyl orange(甲基橙) | red | yellow |
Synthetic indicators: titration(sharp change of colour)
Bases & Alkalis
==base==: Proton acceptor(?)
==alkali==: soluble base
pH>7
Bases are usually oxides or hydroxides of metals
Ammonium salt + alkali -> salt + H2O + NH3
(用于检测ammonium ion,followed by 氨气的检测(damp潮湿的 red litmus paper turns blue))
7.1.2 The Ions in Acids & Alkalis
pH scale: how acidic or alkaline a solution is
acidity, neutrality, alkalinity
logarithmic对数的
pH(n) -> 氢离子浓度为10^(-n) mol/L
universal indicator: 不同指示剂的混合物。
7.1.3 Proton Transfer, Strong & Weak Acids
H+: proton(氕)
Acids: proton donors
Bases: proton acceptors
strong & weak acids: completely / partially dissociate(ionise)
7.1.4 Classifying Oxides
acidic oxide / basic oxide
酸性氧化物和碱反应。反之亦然
neutral oxide(CO,NO,N2O)
Amphoteric oxide(ZnO, Al2O3)
7.2 Preparation of Salts
7.2.1 Preparing Soluble Salts
sulphate硫酸盐,chloride氯化物
filtrate: 过滤后的液体
Insoluble base: Dissolving
use spatula to add excess CuCO3 into a beaker of HCL until no further bubbling or no further dissolving
filter off the excess solid(取filtrate)
heat the salt solution to evaporate water
cool the saturated solution to form crystal
wash the crystal with distilled water
dry the crystal with filter paper

Soluble base: Titration
记得看syllabus!!
-> Add alkali + indicator to conical flask using a pipette
-> Add acid to burette, noting the starting volume
-> add acid to alkali slowly until indicator changes colour
-> calculate
Use volumetric pipette to transfer 25cm3 of HCl(aq) into a conical flask
Add a few drops of methyl orange indicator
fill a burette with NaOH(aq)
add NaOH(aq) from the burette to the conical flask until the end point - Orange
repeat the process without indicator, but using the same volume of acid and alkali as used in the titration
heat the salt solution to evaporate water
cool the saturated solution to form crystal
wash the crystal with distilled water
dry the crystal with filter paper

7.2.2 Preparing Insoluble Salts
precipitation reaction
the reactants must be soluble
mix AgNO3(aq) and NaCl(aq) solution in a beaker
filter the solution to collect the insoluble salt
wash the crystal with distilled water
dry the crystal with filter paper

7.2.3 Solubility Rules
Soluble: K, Na, NH4
Soluble: NO3(硝酸)(Nitrate)
Cl(默认可溶): Ag,Pb ,Hg
SO4(默认可溶): Ba, Ca, Pb , Ra, Sr
CO3(默认不可溶): 除了钾钠氨
OH(默认不可溶): 除了钾钠氨,Ca(partially), Ba
默认不可溶: OH(CaOH partially soluble,Ba(OH)2), CO3
heat transfer: particle to particle transfer
描述粒子运动:先random
7.2.4 Hydrated & Anhydrous Salts
Hydrated salts: salts that contain water within their structure
Anhydrous sats: contain no water in their structure
dehydrated: 脱水
Water of crystallisation: water molecules included in the structure of some salts during the crystallisation process
Color change:
第一主族和第二主族没什么颜色。要记得color change两个:copper sulfate 蓝色到白色;cobalt(II) chloride 粉色到蓝色
8. The Periodic Table
8.1 The Periodic Table & Trends
8.1.1 The Periodic Table
order: Increasing atomic number
group: 族
period: 周期(electron shells)
group 0第八组
Valency
Valency(combining power): how many bonds an atom can make with another atom or how many electrons its atoms lose, gain or share, to form a compound(化合价)
8.1.2 Periodic Trends
The metallic character左下最强,右上最弱
metalloids / semi-metals(准金属): shows some of the properties of metals and some of non-metals
transition elements are denser than group I elements
8.2 Group Properties & Trends
8.2.1 Group I Properties
(alkali metals)
soft and easy to cut
shiny silvery surfaces
conduct heat and electricity
low m.p. and low density (越往下m.p.越低)
8.2.2 Group VII Properties
(halogens)
poisonous
diatomic
halide ions
Cl2(Chlorine): pale yellow-green gas
Br2(Bromine): red-brown liquid
I2(iodine): grey-black solid
the outer electrons are closer to the nucleus so there are stronger electrostatic forces of attraction
越往下颜色越深
8.2.3 Group VII Displacement Reactions
halogen displacement reaction
I2 vapour: purple
I2 aqueous: brown
8.2.4 Transition Elements
hard and strong
good conductors of heat and electricity
high m.p. highly dense
form coloured compounds and often have more than one oxidation state(pigments颜料)
catalysts催化剂
limb and joint replacement
dyes and paints, stained glass jewellery
8.2.5 Noble Gases
Group 0
low m.p. and b.p.
monoatomic, colourless gasses
full outer shells
extremely stable (unreactive and inert)
9. Metals
9.1 Properties, Uses & Alloys of Metals
9.1.1 Properties of Metals
半金属:semimetals, metalloids
metal bond的强度可以由沸点得出(气体时原子都分开)
Properties of metals
- conduct heat and electricity(sea of delocalized electrons)
- malleable(can be hammered and made into different shapes压扁成一片) and ductile(can be drawn into wires(延展性))
- lustrous & shiny
- high density, high m.p. (metallic bond -determined by-> number of delocalized electrons)
- form positive ions, basic oxides
- solid(except mercury)
Properties of non-metal
- Do not conduct heat and electricity(insulator)
- brittle(脆) when solid
- dull and nonreflective
- low density and low m.p. (low的都是simple molecules. Giant covalent molecules还是很强的(diamond
3200, graphite3400, silicon dioxide~2000))(看到3000优先想钻石石墨) - form negative ions, acidic oxides
- solid, liquid(Br2…), gas
金属+冷水 -> 金属氢氧化物 + 氢气
金属+蒸汽 -> 金属氧化物 + 氢气
和酸:置换反应
和氧气:氧化物
9.1.2 Uses of Metals(Al, Cu)
Uses of Al:
(most abundance)(form a layer of aluminium oxide, which acts as a protective layer)
| Use | Most Important Property |
|---|---|
| Aircrafts bodies | High strength-to-weight ratio, Low density |
| Overhead power cables | Good conductor of electricity, Low density |
| Saucepans | Good conductor of heat |
| Food containers | Non-toxic, Resistant to corrosion and acidic food stuffs |
| Window frames | Resistant to corrosion |
Uses of Cu:
| Use | Most Important Property |
|---|---|
| Electrical wires | Good conductor of electricity, High ductility |
| Water pipes | Easy to bend, Non-toxic, Unreactive |
9.1.3 Alloys(合金)
Alloys: mixture of metal with other elements
| Alloy | Components | Use | Reason 4 Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brass | Cu+Zn | Musical instruments, Ornaments(饰品), Door knobs | Hard, Malleable |
| Stainless steel | Fe+Others(Cr, Ni, C) | Cutlery(切具) | Hard, Resistant to corrosion |
Cr可以让成品更shiny, 好看
Alloys通常harder, stronger, more useful, resistant to corrosion / extreme temperatures
Structure
Metal: regular arrangement of ions
Alloys: irregular arrangement of atoms
The metal lattice structure is distorted(扭曲) in alloys
Reason 4 the Properties
atoms of different sizes -> distorts the normally regular arrangements of atoms in metals -> more difficult for the layers to slide over each other -> harder / stronger
9.2 Reactivity Series & Corrosion of Metals
9.2.1 Reactivity Series
方法:displacement reactions(substitution)
K,Na,Ca,Mg,Al,(C),Zn,Fe,(H),Cu,Hg,Ag,Pt,Au
钾钠钙(钙钠)镁铝
(碳)锌铁(氢)
铜汞银铂金

四种金属反应
Metal + Acid -> Salt + Hydrogen:氢之前
Metal+ Water-> Hydroxide + Hydrogen:钾钠钙
Metal + Steam -> Oxide + Hydrogen:氢之前
Metal + Oxygen -> Oxide:氢之前+铜
CuO:黑的
9.2.2 Explaining Reactivity
Al: a protective layer of aluminium oxide which is very thin (prevents reaction with water and dilute acids)
9.2.3 Rusting of Iron
Rusting: Iron专属 Corrosion: 所有metal都有
iron + water + oxygen -> hydrated iron(III) oxide(氧化铁)
防止生锈:barrier methods, painting, plastic coating(还有后面的两个)
grease: oil
paint: plastic
iron & steel: rust
other metal: corroded
9.2.4 Galvanising & Sacrificial(牺牲) Protection
Sacrificial protection: a more reactive metal can be attached to a less reactive metal
zinc is sacrificed to protect the steel
electrons travel from the zinc to th
galvanising(镀锌): a process where the iron to be protected is coated with a layer of zinc
9.3 Extraction of Metals
9.3.1 Extraction of Metals
Metal ore: a rock that contains enough of the metal to make it worthwhile extracting
Methods:
- Electrolysis aqueous solutions containing their ions
- using blast furnace / react with more reactive material
- 碳之下:和碳或一氧化碳还原
- 碳之上:电解熔融氧化物/氯化物 (贵)
Reduction: 很多矿石是氧化物。移除氧是还原反应
Native metals: gold, platinum(chemical stability, 不用提取)
9.3.2 Extraction of Iron from Hematite(赤铁矿)
Ores: Hematite(Fe2O3), Magnetite(Fe3O4), Fayalite (Fe2SiO4)
blast furnace
coke(C), hematite(Fe2O3, SiO2), limestone(CaCO3)
- burning of carbon to provide heat and produce CO2(Waste) C+O2 -> CO2 (exothermic)
- Reaction of carbon dioxide to carbon monoxide C+CO2 -> 2CO (Good reducing agent)
- Reduction of iron(III) oxide by carbon monoxide Fe2O3 + 3CO -> Fe(l) + 3CO2
- Thermal decomposition of calcium carbonate / limestone to produce calcium oxide CaCO3 -> CaO(s)+CO2
- Formation of slag(不要的那些impurities) CaO + SiO2(s) -> CaSiO3(l)
Slag比Iron轻
写方程式记得铁和slag是liquid, CaO是solid
9.3.3 Extraction of Aluminium from Bauxite(!)
Al2O3
Electrolysis
(~2000°C)Molten aluminium oxide (impure) / bauxite + cryolite
2000°C加了cryolite降到1000°C
Cryolite可以1. 增加导电性 2. 降低操作时的温度
电极用石墨
Cathode: Al3+ + 3e- -> Al(在cell底部(siphoned(虹吸) off from time to time))
Anode: 2O2- -> O2 + 4e- (need to be regularly replaced (reacts with oxygen))
贵->用很多电

10. Chemistry of the Environment
Simon 学案
10.1 Water & Water Pollution
10.1.1 Water: Chemical Tests
10.1.2 Substances in Water from Natural Sources
10.1.3 Water Treatment
10.1.4 Fertilisers
10.2 Air Quality & Climate
10.2.1 Air
10.2.2 Effects of Greenhouse Gases
10.2.3 Reducing the Effects of Environmental Issues
10.2.4 Photosynthesis
11. Organic Chemistry
Organic Chemistry: The scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds.
(老师ppt上): the study of structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-containing compounds. (excluding simple compounds like CO, CO2, CO3^2-^)
Most organic compounds contain carbon and hydrogen m but they may also include any number of other elements, such as nitrogen, oxygen, halogens, phosphorus, silicon, and sulfur
11.1 Formulae, Functional Groups & Terminology
11.1.1 Organic Formulae
Organic compounds: those which contain carbon (不包括metal carbonates, carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide)
Hydrocarbon: a compound that contains only hydrogen and carbon atoms
表示方法:empirical formula, displayed formulae, general formulae, structural formulae
Empirical Formula(C2H5): simplest ratio of atoms
Molecular Formula(C4H10): Actual number of atoms of each element in a compound
Displayed Formulae(a diagram): shows the spatial arrangement of all the atoms and bonds in a molecule
**Structural Formulae(CH3CH2CH2CH3): **shows the order and arrangement of atoms
- only show important bonds(double and triple bonds)
- identical groups / side groups: 打括号
*Skeletal Formula: All C, H and C-H bonds are removed
structure isomers: same molecular formulae, different structural formulae (structural isomerism)
如果是CnH2n考虑两种情况,double bond 或者 ring !!!!!
carbon: can form 4 bonds
11.1.2 Homologous Series
Functional Group: an atom or group of atoms which are bonded in a specific arrangement that is responsible for the characteristic reactions of each member of a homologous series.
-> dictates their physical and chemical properties
Homologous Series: a family of organic compounds that have similar features and chemical properties due to them have the same functional group
-> same functional group
-> same general formula
-> similar chemical properties
-> gradual change in physical properties
-> differing form one member to the next by a -CH2- unit
| Family(Homologous Series) | 中文 | Functional Group | Suffix/Preffix | General Formulae | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alkane | 烷 | C-C | -ane | C | Methane |
| Alkene | 烯 | C=C | -ene | C | Ethene |
| Alkyne | 炔 | C≡C | -yne | C | Ethyne |
| Halogenoalkane | -X | halo- (fluoro-, chloro-, bromo- ) | C | Fluoromethane | |
| Alcohol | 醇 | -OH | -(an)ol | C | methanol |
| Carboxylic Acid | -COOH | -(an)oic acid | C | methanoic acid | |
| Ester | -COO- | -yl-anoate | methyl methanoate |
General Formula: A type of empirical formula that represents the composition of any member of a whole homologous series of organic compound
General Characteristic of Homologous Series:
-> The same general formulae
-> same functional group
-> similar chemical properties
-> Gradation in their physical properties
-> The difference in the molecular formula between one member and the next is CH2
Meth, Eth, Prop, But (Monkeys Eat Peeled Bananas)
11.1.3 Saturated & Unsaturated Compounds
Saturated compounds: have molecules in which all carbon-carbon bonds are single bonds (e.g. alkanes)
Unsaturated compounds: consist of molecules in which one or more carbon-carbon bonds are not single bonds (e.g. alkenes, carboxylic acid)
11.1.4 Naming Organic Compounds(!)
Substituents: 替换掉有机物里的氢的东西(比如CH4去掉一个H加一个F)
IUPAC: International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry
IUPAC naming system: Prefix - Parent - Suffix
-> Prefix: Name and position of substituents
-> Parent: Length of the longest carbon chain
-> Suffix: Main functional group
两个部分:the stem, end part (prefix, suffix)
The stem: indicates the number of carbon atoms present in the longest continuous chain of the compound
| # of C in the longest chain | The stem |
|---|---|
| 1 | meth |
| 2 | eth |
| 3 | prop |
| 4 | but(u读you的音) |
| 5 | pent |
| 6 | hex |
| 7 | hept |
| 8 | oct |
| 9 | non |
| 10 | dec |
| 11 | undec |
| 12 | dodec |
Substituent
| Alkyl Group | Structural Formula | Name |
|---|---|---|
| -CH3 | -CH3 | Methyl |
| -C2H5 | -CH2CH3 | Ethyl |
| -C3H7 | -CH2CH2CH3 | Propyl |
| -C4H9 | -CH2CH2CH2CH3 | Butyl |
| # of substituents | Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Mono |
| 2 | Di |
| 3 | Tri |
| 4 | Tetra |
| 5 | Penta |
例子: 2-methylbutane 2,3-dimethylbutane
The end part: tells you what functional group is in the compound
| End part of the name | Functional group | Organic family |
|---|---|---|
| ane | none (contains only C-C bonds) | Alkane |
| ene | C=C bond | Alkene |
| anol | –OH | Alcohol |
| anoic acid | –COOH | Carboxylic acid |
| amine | –NH2 | Amine |
| -yl -anoate | –COO– | Ester |
butanoic acid
propene
pentanol
高级命名法
需要指定functional group出现在哪一个carbon atom 上面(数字越小越好)
-an: 单键 -en: 双键
在propene之后,要指定双键出现在哪里(e.g. but-1-ene, but-2-ene)
-OH: alcohol / hydroxyl group
和ene一样,在ethanol之后要指定在哪(e.g. propan-1-ol, propan-2-ol)
carboxylic acid很伟大,不用指定。默认出现在1号位
Ester: 基于原先的alcohol和carboxylic acid,比较复杂,和structure的画法相反
原子越多燃烧放出的re’liang
11.2 Organic Families(!)
11.2.1 Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels: release a large amount of energy when burned
三大类:Coal / Natural Gas(主要是CH4) / Petroleum (mixture of hydrocarbons)
petroleum的分离方式:fractional distillation
气体从塔下面被heater加热后,顺着塔向上走
塔从下往上的趋势:
-> lower boiling point
-> decreasing chain length
-> higher volatility (挥发性)
-> lower viscosity (流动性)
| Temp | Name | Use |
|---|---|---|
| 20 | Refinery Gas | for gas used in heating and cooking |
| 40 | Gasoline | for fuel used in cars |
| 110 | Naphtha(石脑油) | as chemical feedstock |
| 180 | Kerosene / Paraffin(煤油) | for jet fuel |
| 260 | Diesel oil / Gas oil(柴油) | for fuel used in diesel engines |
| 280 | Fuel oil | for fuel used in ships and home heating systems |
| 300 | Lubricating oil | for lubricants, waxes and polishes |
| 340 | Bitumen(沥青) | for making roads |
11.2.2 Alkanes(烷烃)
saturated hydrocarbons
CnH2n+2
cycloalkanes会少两个H
物理性质:
b.p.和m.p.:
-> 分子越大bpmp越大
-> chain越straight(没什么branches)bpmp越大
Solubility:
-> Insoluble
化学性质:
Unreactive
-> C and H have similar electronegativities
-> strong and non-polar C-C and C-H bonds
想要react的话也有
-> Combustion(燃烧): Carbon dioxide / monoxide
Reagents 1: Excess O2 (Complete combustion)(reagent:和reactant差不多,是加入到原本物质的一方)
Reagents 2: Limited O2 (Incomplete combustion) (就是氧气没那么足)
Conditions: Room temperature
Equation 1: CxHy + O2 ---> x CO2 + y H2O (O2要配平) (Complete, 燃烧产生CO2)
Equation 2: CxHy + O2 ---> x ==CO== + y H2O (O2要配平) (Incomplete, 燃烧产生CO)
-> Substitution(比如一个H变成Cl) : Halogenoalkanes
reactions in which one atom or group of atoms is replaced by another atom or group of atoms
具体来说,这里的substitution是==halogenation== (把一个东西换成halogen)
Reagents: Halogens(Cl2 , Br2 …)
Conditions: ==Ultraviolet light==
Equation: CH4 + Cl2 —(UV light)—> CH3Cl + HCl (把一个H换成Cl) (CH3Cl: ==Chloromethane==)
(有UV light参与所以也是photochemical reaction)
-> Cracking (断键) : Alkenes + Alkanes or Hydrogen
High temp. & press. (or catalyst + heat)
11.2.3 Alkenes(!!)
11.2.4 Addition Reactions(!!)
11.2.5 Alcohols
Alcohol: One or more H atoms in an alkane have been replaced by OH groups
General formula: CnH2n+1OH
Physical properties:
-> soluble in water
-> High boiling point (78 for ethanol)
Usage:
-> solvent
-> Fuel
Reactions:
->
Alkenes —(Catalytic Addition of H2O(g))—> Alcohols
Glucose —(Fermentation)—> Alcohols
Alcohols —> Combustion (CO2/CO) / Oxidation(Carboxylic acids) / Esterification(Esters)
Forming
-> Hydration
CH2=CH2 + H2O(steam, g) —(H3PO4 , 300C, 60atm) —> CH3CH2OH
High Purity, High yield, Non-renewable, Continuous flow process, one product formed
High energy cost
-> Fermentation
C6H12O6(Glucose) —(Yeast, 25C35C) —> 2C2H5OH + 2CO2~
High alcohol kills the yeast! (12% ~ 17%) , Renewable, low energy cost
batch process (fixed amount) , Occupied space
Beers / Wines
Reacting
-> Combustion
C2H5OH + 3O2(Excess) —> 2CO2 + 3H2O
C2H5OH + 2O2(Limited) —> 2CO + 3H2O
-> Oxidation
Acidified potassium dichromate(VI) - K2Cr2O7
Orange to Green (Cr2O7^2-^ -> Cr^3+^)
Acidified potassium manganate(VII) - KMnO4
Purple to Colourless (MnO4^-^ -> Mn^2+^)
Conditions: Heat under reflux
Equation: CH3CH2CH2(OH) + 2[O] —(reflux / H^+^) —> CH3CH2COOH + H2O
-> Bacterial Oxidation
Reagents: O2
Equation: CH3CH2CH2(OH) + O2 —(Enzymes in bacteria) —> CH3CH2COOH + H2O
(production of vinegar)
Reflux Heating
A solution may be heated to a boiling point without losing the solvent to evaporation
Increasing the number of vaporization - condensation cycles that the vapor undergoes
-> Esterification
conditions: concentrated H2SO4 or H3PO4
CH3CH2OH + CH3CO2H —(H^+^, reflux) —> CH3CO2CH2CH3 + H2O
11.2.6 Carboxylic Acids
Physical properties:
-> b.p.随分子大小的增加而增加
-> b.p. 比对应大小的alkene更高
-> soluble in water
-> high b.p.
Reaction:
redox with metals -> Carboxylates
neutralization with alkalis -> Carboxylates
acid-base with carbonates -> Carboxylates
Esterification -> Esters
-> Redox with metals
2CH3CO2H + 2Na —> 2CH3CO2Na + H2
sodium ethanoate: CH3CO2Na
-> Neutralization with Alkalis
CH3CO2H + NaOH —> CH3CO2Na + H2O
-> Acid-base with Carbonates
2CH3CO2H + Na2CO3 —> CH3CO2Na + CO2 + 2H2O
-> Esterification
CH3CO2H + CH3CH2OH —(H^+^, Reflux) —> CH3CO2CH2CH3 + H2O
CH3CO2CH2CH3: ethyl ethanoate
和上面的一样
11.2.7 Ethanoic Acid & Esterification Reactions
11.3 Polymers(!)
11.3.1 Polymers
11.3.2 Addition & Condensation Polymers
11.3.3 Plastics & their Disposal
11.3.4 Proteins
12. Experimental Techniques & Chemical Analysis
Polystyrene Cup: minimize th
12.1 Experimental Techniques
12.1.1 Apparatus for Measurements
time: stopwatch
temp: thermometer / digital probe
mass: digital balance(needs to be tared(set to zero))
volume-liquids
(measuring cylinders)
graduated: 带有刻度的

volume-gases

Advantage & Disadvantage

12.1.2 Solutions

residue [ˈrezɪdjuː]
12.1.3 Acid-Base Titrations
细节懒得写了
Common acid-base indicators
| Indicator | Colour in acid | Colour in alkali | Colour in neutral |
|---|---|---|---|
| Litmus solution | Red | Blue | Purple |
| Red litmus paper | Stays red | Turns blue | No change |
| Blue litmus paper | Turns red | Stays blue | No change |
| Methyl orange | Red | Yellow | Orange |
| Phenolphthalein | Colourless | Pink | Colourless |
| Thymolphthalein | Colourless | Blue | Colourless |
12.2 Separation & Purification
12.2.1 Paper Chromatography(色谱法)
used to separate substances that have different solubilities in a given solvent
capillary action: 毛细效应

12.2.2 Locating Agents & Rf Values
locating agents: react with the sample and produce a coloured product which is then visible
Rf Value(Retention Factor): distance travelled by substance / distance travelled by solvent

12.2.3 Separation & Purification Techniques
Filtration
used to separate an undissolved solid from a mixture of the solid and a liquid / solution

Crystallisation
used to separate a dissolved solid from a solution, when the solid is more soluble in hot solvent than in cold
saturated solution: 饱和溶液
(dipping a clean, dry, cold glass rod into the solution)

(还要用distilled water to remove any impurities and then allowed to dry)
Simple Distillation
used to separate a liquid and soluble solid from a solution
冷凝管:condenser

Fractional Distillation
fractionating column
thermometer: 温度计
Assessing purity
Pure substances: melt and boil at specific and sharp temp
Mixtures: a range of melting and boiling points
如果样本不纯:b.p.更高m.p.更低
12.3 Identification of Ions & Gases
12.3.1 Identification of Anions

12.3.2 Identification of Cations

| Additional Method | KMnO4 | |
|---|---|---|
| Cl- | ||
| Br- | No color | |
| I- | Change orange |
(Al,Zn)Excess->amphoteric(两性的)可以和碱反应
Clear: 像水一样可以看穿
Colourless: 没有颜色
flame test: blue Bunsen flame
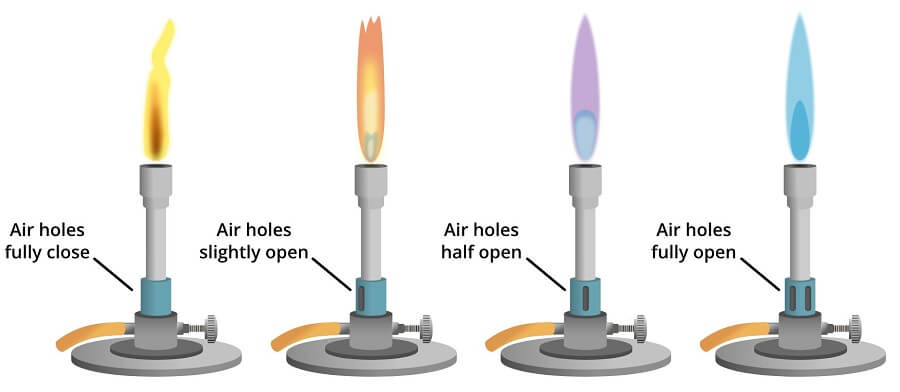


12.3.3 Identification of Gases

神秘化学知识
离子:
| Cr3+ | Green | |
| Mn2+ | Pink | |
| Fe2+ | Green | |
| Fe3+ | Orange | |
| Ni2+ | Green | |
| Cu2+ | Blue | |
| Co2+ | Pink | |
| Zn2+, Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+ | Colourless |
区分Cl, Br, I的方法
| Cl- | Br- | I- |
|---|---|---|
| white | cream | yellow |
| +Nh3 dissolve! | x | x |
| x | x | +H2O2 yellow solution bubbling |
| x | +KMnO4 yellow solution | +KMnO4 Brown solution |
Reference
Other internet resources …
